Extension cords are essential tools for providing power to appliances and electronics that are located far from electrical outlets. Understanding how extension cords are wired can help prevent electrical hazards and ensure safe usage.
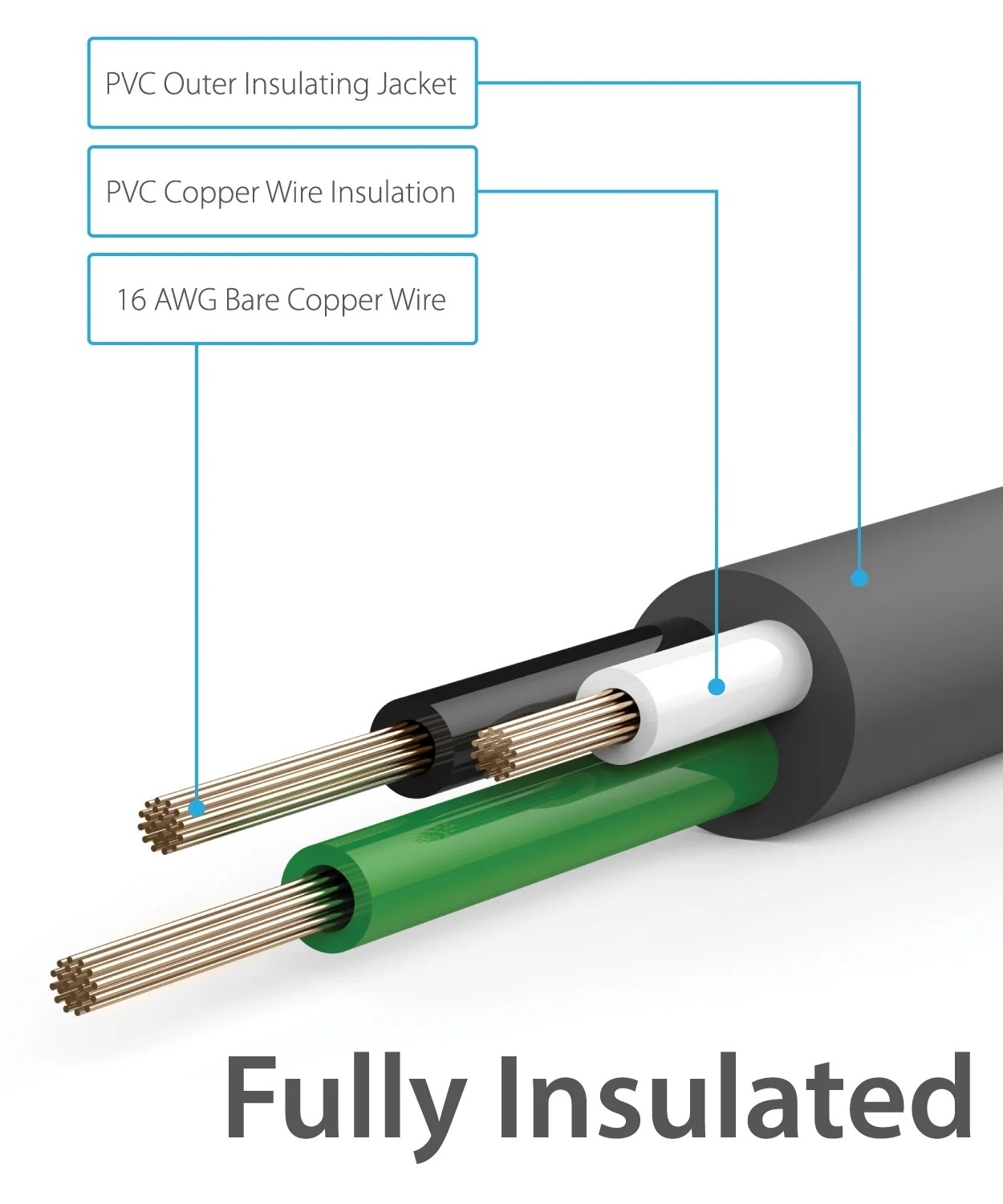
Extension cords typically consist of three wires: a hot wire, a neutral wire, and a ground wire. The hot wire carries the electrical current, the neutral wire completes the circuit, and the ground wire provides a path for electrical currents in case of a short circuit.
 How To Read An Extension Cord Wiring Diagram Moo Wiring (moowiring.com)
How To Read An Extension Cord Wiring Diagram Moo Wiring (moowiring.com)
When wiring an extension cord, it is important to match the wire colors correctly. The hot wire is usually black or red, the neutral wire is white, and the ground wire is green or bare copper. Make sure to connect the wires to the corresponding terminals in the plug and receptacle to ensure proper function.
It is also important to use the correct gauge of wire for the intended purpose of the extension cord. Thicker wires have a lower gauge number and can handle higher currents, while thinner wires have a higher gauge number and are suitable for lighter loads. Using the wrong gauge of wire can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
When connecting the wires to the plug and receptacle, make sure to secure them tightly to prevent loose connections. Loose connections can lead to arcing and overheating, which can cause damage to the extension cord and increase the risk of electrical fires.
In conclusion, understanding the wiring diagram of an extension cord is essential for safe and proper usage. By following the correct wiring practices and using the appropriate gauge of wire, you can ensure that your extension cord operates safely and effectively. Remember to always inspect your extension cords for any signs of wear or damage before each use to prevent accidents and ensure electrical safety.